Diffusion-Relaxation Suite
MRI generates images with millimeter-scale spatial resolution, while many important biological features occur at much smaller (microscopic) scales. Over the past several decades, MRI practitioners have used the information derived from biophysical parameters (like relaxation and diffusion) to indirectly probe microscopic tissue compartments using millimeter-scale data. While these approaches have been somewhat successful, a new paradigm has recently emerged that leverages multiparametric MRI data (e.g., using relaxation and diffusion jointly in a higher-dimensional experiment) to probe tissue microstructure with an unprecedented level of detail.
Diffusion-Relaxation Suite (DRSuite) is an open-source software package that provides novel analysis methods to identify and separate multiple microstructural tissue compartments from MRI data using advanced constrained estimation techniques. These form the central component of an end-to-end package that includes novel tools for multicontrast image registration, spectroscopic image estimation from multicontrast MRI data, and spectroscopic image visualization. This package also provides tools to quantify the expected spectral information produced by a multiparametric acquisition, which can be used for quality assessment and protocol optimization.
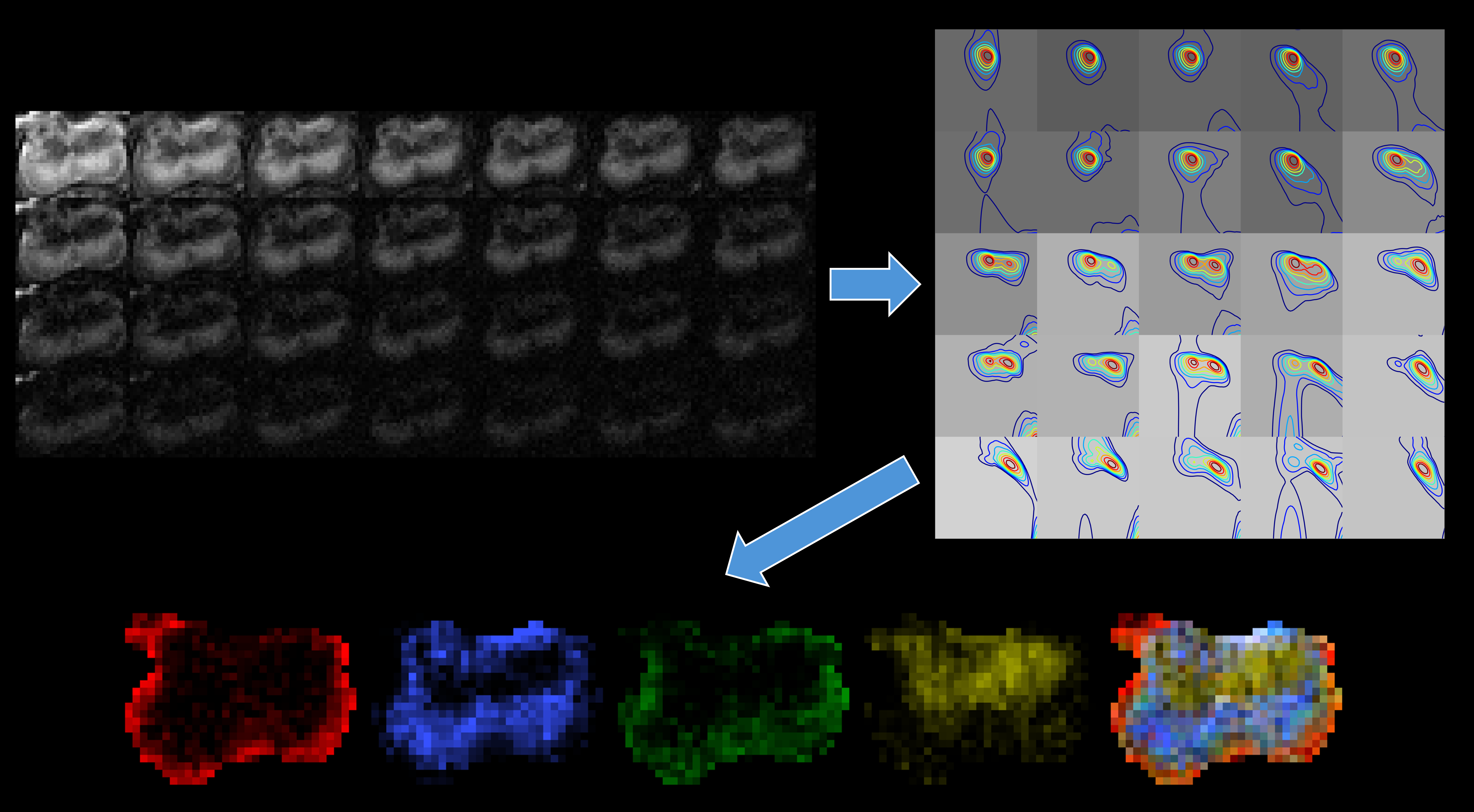
Example of 2D spectrum estimation |

Example of 1D spectrum estimation |

DRSuite architecture |
DRSuite’s functionality includes the following:
Spatially-regularized spectrum estimation. We provide an implementation of the spatially-regularized multiparametric spectrum estimation techniques described in:
Kim, E. K. Doyle, J. L. Wisnowski, J. H. Kim, J. P. Haldar. Diffusion-Relaxation Correlation Spectroscopic Imaging: A Multidimensional Approach for Probing Microstructure. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 78:2236-2249, 2017. <https://dx.doi.org/10.1002/mrm.26629>
Kim, J. L. Wisnowski, C. T. Nguyen, J. P. Haldar. Multidimensional Correlation Spectroscopic Imaging of Exponential Decays: From Theoretical Principles to In Vivo Human Applications. NMR in Biomedicine 33:e4244, 2020. <https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.4244>
Liu, D. Mandal, C. Liao, K. Setsompop, J. P. Haldar. An Efficient Algorithm for Spatial-Spectral Partial Volume Compartment Mapping with Applications to Multicomponent Diffusion and Relaxation MRI. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging 11:1283-1293, 2025. <https://doi.org/10.1109/TCI.2025.3609974>
Spatially-regularized spectrum estimation enables major improvements, both theoretically and empirically, relative to earlier methods designed to estimate diffusion/relaxation spectra. DRSuite currently supports both 1D spectrum estimation from one-dimensional contrast encoding (a common, relatively-easy experiment to implement) as well as 2D spectrum estimation from higher-dimensional diffusion-relaxation or relaxation-relaxation contrast encoding (a more advanced experiment that offers substantially better microstructure resolving power).
Visualization. We provide visualization tools that allow users to plot spatial-spectral images, and obtain spatial maps of different microstructural features by integrating over different regions of the spectral dimension.
Phantom Data. We also provide tools for generating synthetic multidimensional phantom datasets with known ground-truth spectra. These datasets can be used to evaluate and compare different acquisition schemes and spectrum estimation methods.
Estimation-theoretic characterization. We provide a tool to evaluate estimation-theoretic Cramér-Rao bounds for this type of spectrum estimation. This provides a quantitative measure that can be used for evaluating the quality of estimated spectra, and can also be used to prospectively assess the estimation-theoretic characteristics of different experimental acquisition paradigms. This can be very useful for designing and optimizing experiments, as described in:
Kim, J. L. Wisnowski, C. T. Nguyen, J. P. Haldar. Multidimensional Correlation Spectroscopic Imaging of Exponential Decays: From Theoretical Principles to In Vivo Human Applications. NMR in Biomedicine 33:e4244, 2020. <https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.4244>
Kim, J. L. Wisnowski, J. P. Haldar. Improved Efficiency for Microstructure Imaging using High-Dimensional MR Correlation Spectroscopic Imaging. Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers, Pacific Grove, 2017, pp. 1264-1268. <https://doi.org/10.1109/ACSSC.2017.8335555>
Kim, J. P. Haldar. Faster Diffusion-Relaxation Correlation Spectroscopic Imaging (DR-CSI) using Optimized Experiment Design. International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 25th Annual Meeting, Honolulu, 2017, p. 176. <https://archive.ismrm.org/2017/0176.html>
This website hosts the DRSuite documentation, the software itself is available from GitHub
DRSuite can be cited as:
Mandal, A. A. Joshi, D. W. Shattuck, J. P. Haldar. “Diffusion-Relaxation Suite.” [Computer Software]. Available: https://drsuite.org/.
Development Team
Debdut Mandal, Anand A. Joshi, David W. Shattuck, Justin P. Haldar (PI)
Support
Development of this software was supported in part by NIH grant R56-EB034349.